Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Virtual Dark/Bright Field (VDF/VBF) Imaging#
This example demonstrates how to acquire a VDF/VBF image using DE API.
The virtual images are created by summing or subtracting the pixel values of the input image based on the values of the virtual masks. The virtual masks are 8-bit images with values: - 0: Negative Mask, pixel values subtracted - 1: Default value, pixels not accounted for - 2: Positive Mask, pixel values added
Here we will
Connect to the DE server
Set the hardware ROI
Acquire a single diffraction pattern for guiding the virtual imaging
Automatically generate the virtual birght field (VBF) and virtual dark field (VDF) images by finding the brightest disk in the diffraction pattern and measuring the extent of the disk in the diffraction pattern.
Acquire the VDF/VBF images and plot them.
import numpy as np
from deapi import Client
import time
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter
from skimage.segmentation import flood
from skimage.morphology import dilation, disk
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
client = Client()
if not sys.platform.startswith("win"):
client.usingMmf = (
False # True if on same machine as DE Server and a Windows machine
)
client.connect(port=13240) # connect to the running DE Server
Get A Single Diffraction Pattern#
We will acquire a single diffraction pattern to guide the virtual masks. We can then use the brightest disk in the diffraction pattern to generate the VDF/VBF masks.
print("Acquiring a single diffraction pattern...")
client.scan(enable="Off") # Disable scanning
client.start_acquisition(1)
# wait for the acquisition to finish
while client.acquiring:
time.sleep(1)
print("Acquisition finished.")
img = client.get_result("singleframe_integrated")[0]
Acquiring a single diffraction pattern...
Acquisition finished.
Define a function to automatically find the bright field in the diffraction pattern
def auto_find_bf(img, threshold=0.5, sigma=10, dilation_rad=30):
filtered = gaussian_filter(img, sigma=sigma)
center = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(filtered), shape=filtered.shape)
val = img[center]
mask = img > (val * threshold)
mask = flood(mask, center) # only the center
mask = dilation(mask, footprint=disk(dilation_rad))
return mask
mask = auto_find_bf(img)
Create the Virtual Masks#
We will create the VDF and VBF masks by setting the pixel values in the masks.
print("Creating virtual masks...")
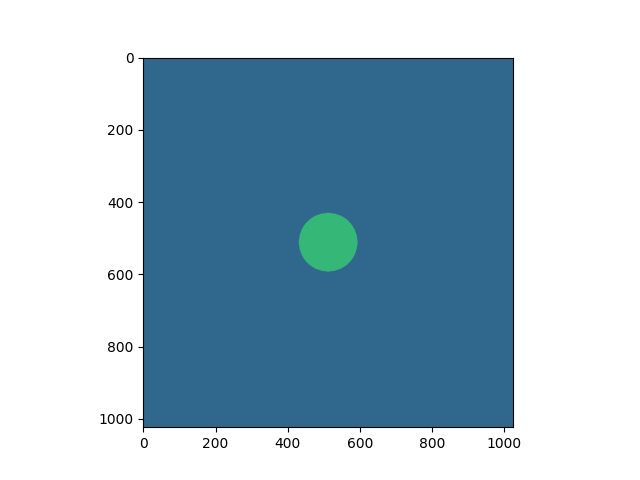
client.virtual_masks[1].calculation = "Sum"
print("Setting calculation")
client.virtual_masks[1].name = "VBF"
client.virtual_masks[1][:] = 1 # Set to 1
client.virtual_masks[1][mask] = 2 # Set mask to 2
print(
"Virtual Mask 1:", client.virtual_masks[1].name, client.virtual_masks[1].calculation
)
client.virtual_masks[1].plot()
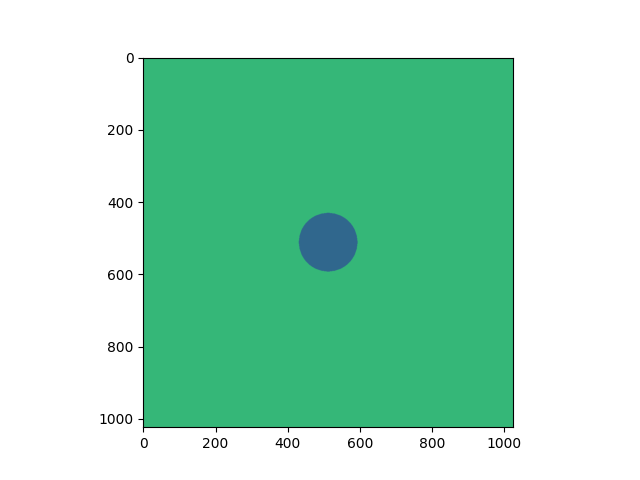
client.virtual_masks[2].calculation = "Sum"
client.virtual_masks[2].name = "VDF"
client.virtual_masks[2][:] = 2
client.virtual_masks[2][mask] = 1
client.virtual_masks[2].plot()
print(
"Virtual Masks:"
f"\nVBF: {client.virtual_masks[1].name} ({client.virtual_masks[1].calculation})"
f"\nVDF: {client.virtual_masks[2].name} ({client.virtual_masks[2].calculation})"
)
Creating virtual masks...
Setting calculation
/home/runner/work/deapi/deapi/deapi/data_types.py:706: UserWarning: Virtual mask shape is not set to Arbitrary. Setting to Arbitrary.
warnings.warn(
Virtual Mask 1: VBF Sum
Virtual Masks:
VBF: VBF (Sum)
VDF: VDF (Sum)
Acquire the Virtual Images#
We will then acquire the virtual images using the virtual masks and plot the results.
client["Frames Per Second"] = 5000 # 5000 frames per second
client.scan(enable="On", size_x=32, size_y=32)
client.start_acquisition()
print("Acquiring virtual images...")
while client.acquiring: # wait for acquisition to finish and then plot the results
time.sleep(1)
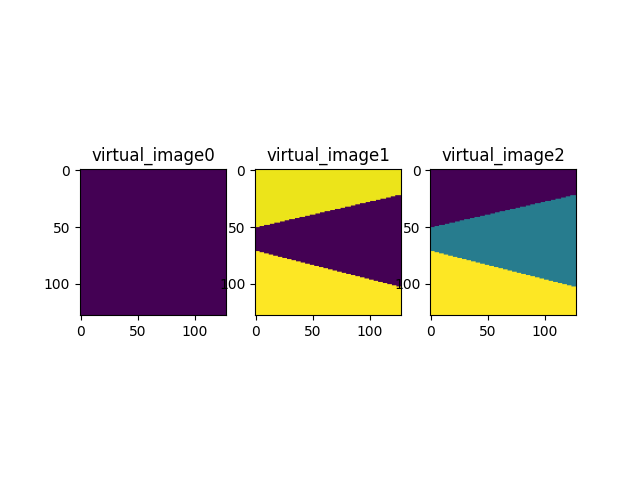
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3)
for a, virt in zip(axs, ["virtual_image0", "virtual_image1", "virtual_image2"]):
data, _, _, _ = client.get_result(virt)
a.imshow(data)
a.set_title(virt)
client.disconnect()
Acquiring virtual images...
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.996 seconds)